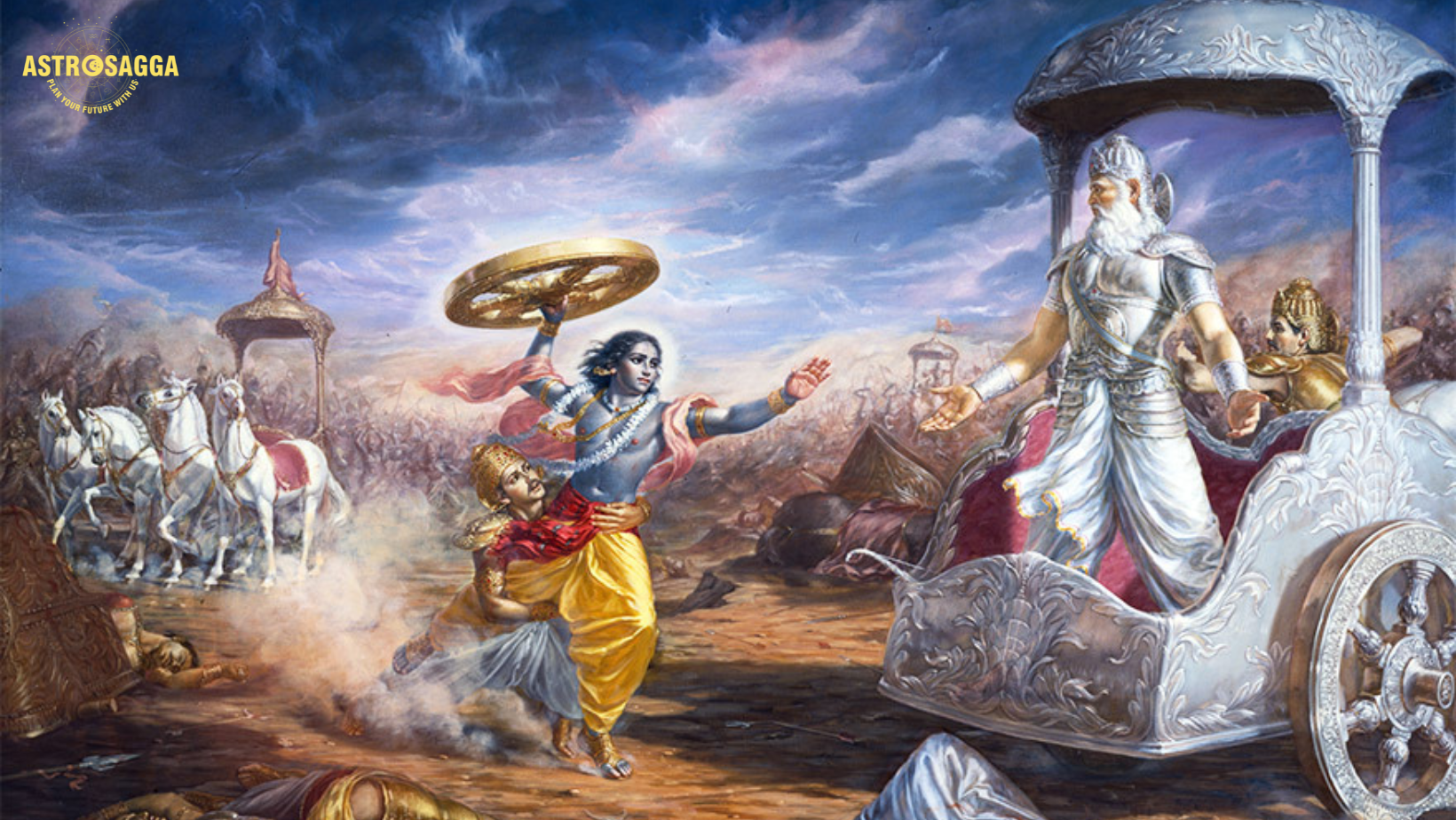
The Bhagavad Gita, a 700-verse Hindu scripture that is part of the Indian epic Mahabharata, is a conversation between Prince Arjuna and the god Krishna, who serves as his charioteer. The text addresses the moral and philosophical dilemmas faced by Arjuna on the battlefield of Kurukshetra. It is a spiritual and philosophical guide that offers profound insights into life, duty, and the nature of reality. Here are seven key learning points from the Bhagavad Gita:
1. The Importance of Dharma (Righteous Duty)
Verse Reference: Bhagavad Gita 2.31
Explanation: Krishna emphasizes the importance of adhering to one's dharma or duty. He tells Arjuna that fighting in the battle is his duty as a warrior and that he should not shy away from it. This highlights the significance of fulfilling one's responsibilities in life, regardless of the challenges involved.
2. Selfless Action (Karma Yoga)
Verse Reference: Bhagavad Gita 2.47
Explanation: Krishna advises Arjuna to perform his duties without attachment to the results. This teaching on Karma Yoga advocates for action driven by a sense of duty, without expecting rewards. It underscores the importance of selfless action as a path to spiritual growth.
3. The Impermanence of the Physical Body
Verse Reference: Bhagavad Gita 2.22
Explanation: Krishna explains that just as a person discards old clothes and puts on new ones, the soul discards an old body and takes on a new one. This teaching on the immortality of the soul and the impermanence of the physical body helps one to transcend the fear of death.
4. The Reality of the Self (Atman)
Verse Reference: Bhagavad Gita 2.20
Explanation: Krishna reveals that the true self (Atman) is eternal, indestructible, and beyond the physical body. This teaching encourages the understanding of the self as distinct from the body, leading to a deeper sense of identity and purpose.
5. Detachment from Material Desires
Verse Reference: Bhagavad Gita 2.71
Explanation: Krishna advises Arjuna to relinquish attachment to material desires and to find peace in detachment. This teaching is crucial for cultivating inner peace and contentment, as attachment often leads to suffering.
6. The Three Gunas (Qualities of Nature)
Verse Reference: Bhagavad Gita 14.5
Explanation: Krishna describes the three gunas—Sattva (goodness), Rajas (passion), and Tamas (ignorance)—as the fundamental forces that influence human behavior. Understanding these qualities helps one to balance them and progress spiritually.
Read Also - What is Vedic Astrology?
7. Devotion and Surrender (Bhakti Yoga)
Verse Reference: Bhagavad Gita 9.22
Explanation: Krishna assures Arjuna that those who worship him with devotion and surrender are always protected. This teaching on Bhakti Yoga emphasizes the importance of devotion and surrender to the Divine as a means of attaining spiritual fulfillment.
Conclusion
The Bhagavad Gita offers timeless wisdom that guides individuals on how to live a life of purpose, integrity, and spiritual growth. These seven teachings provide a foundation for understanding the deeper aspects of life, encouraging self-realization, and fostering a connection with the Divine. By reflecting on these teachings, one can navigate the complexities of life with clarity and strength.
The Bhagavad Gita remains a profound source of spiritual knowledge and practical guidance, applicable to all aspects of life. Each verse carries a wealth of wisdom that continues to inspire and enlighten seekers of truth across generations.